This blogpost describes how I connected my Vaillant VRT350 to OpenHAB.
Introduction
The Vaillant VRT350 uses eBUS (energy bus) for communication with the boiler. The Vaillant VRT350 follows the eBUS standard on the physical layer and uses a Valliant specific extensions on the application layer.
eBUS is a bus, meaning multiple devices can be connected to the same bus. Thus it is possible1 to add your own device to the bus (read: wire) running between the boiler and the thermostat. This coupler can then:
- Read all messages send on the bus.
- Send messages on the bus.
To control the heating installtion from OpenHAB the following is used:
- ESERA automation eBUS Coupler to allow access to eBUS over Ethernet.
- ebusd (ebusdeamon) to handle eBUS communication.
- Exec Binding serves as interface between OpenHAB and ebusd.
Hardware
Hardware used
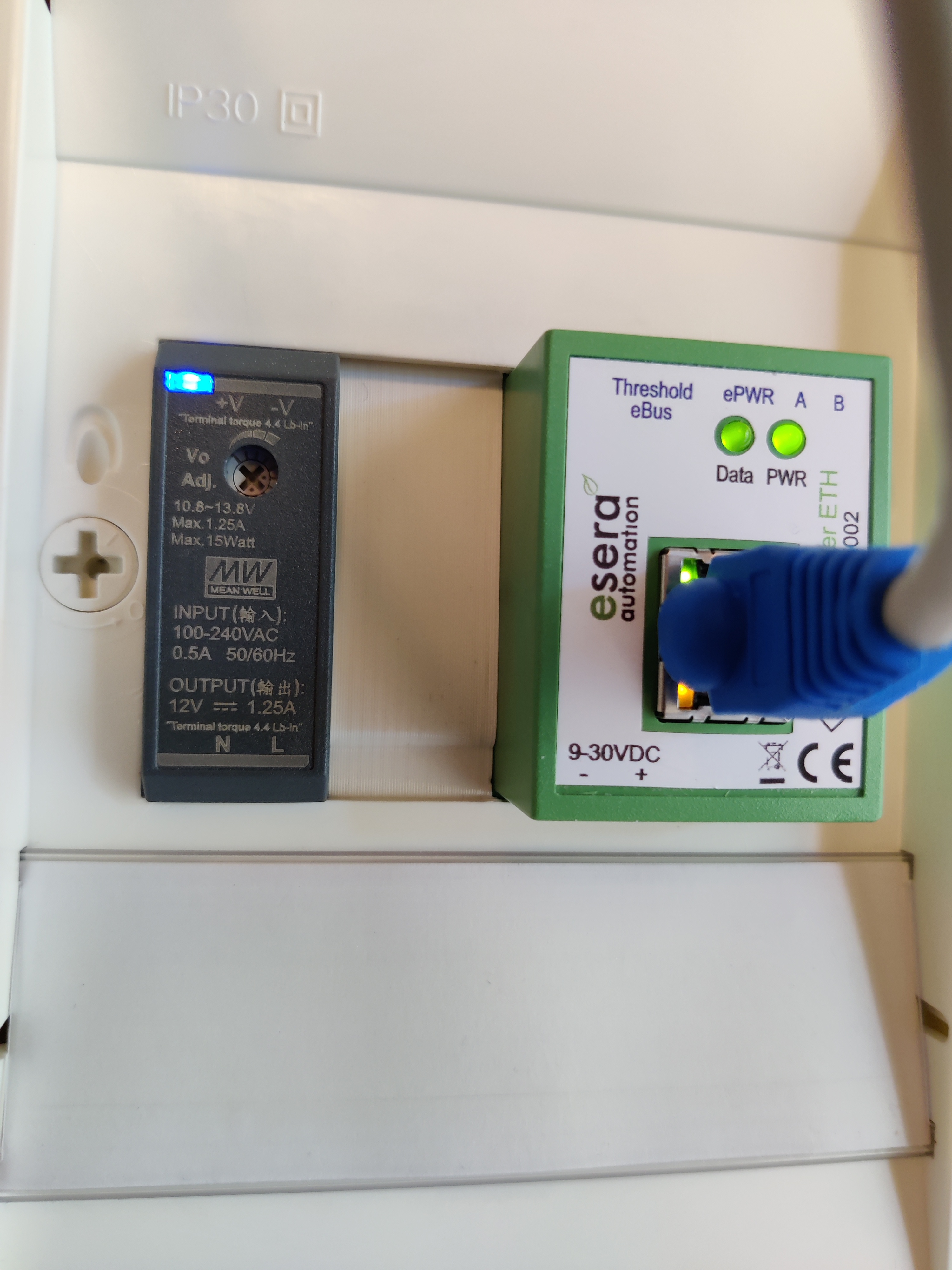
Since my thermostat nor my boiler is near my Raspberry Pi running OpenHAB I’m using the ESERA automation eBUS Coupler Ethernet:

Configuration
The voltage on the eBUS representing a logical 0/1 varies depending on conditions, including wire length. The ESERA eBUS Coupler Ethernet has a small dial (called Trimmer for signal level in the manual which can be adjusted with the supplied Philips screwdriver. This dial adjusts the coupler to the voltages for your installation. Once connected I adjusted the dial until the “Data” led started blinking. If the led is continuously off/on than the devices only sees a 0/1 on the bus. The Vaillant VRT350 regularly communicates with the boiler so data is more or less continuously going over the bus if the boiler and thermostat are on.
eBUSdeamon frequently reported CRC errors. Those where resolved with some further fine adjustment of the screw.
The ESERA eBUS Coupler Ethernet shipped with a software application for configuration. I had to adjust the Serial data packing conditions to avoid connection timeouts in eBUSdeamon. Note a timer of 1ms is probably causing unnecessary network overhead.
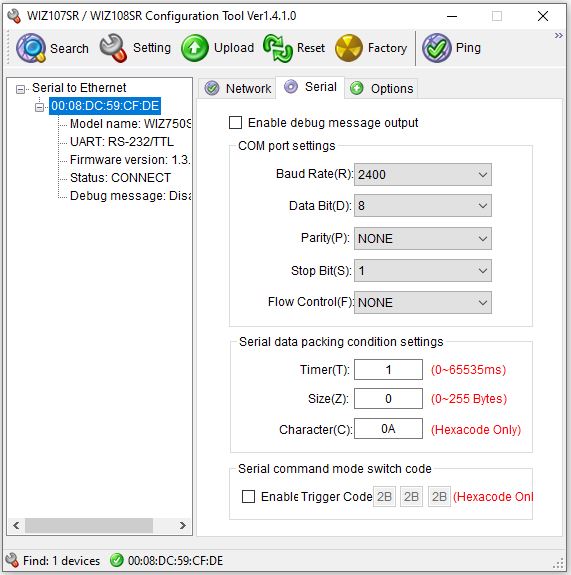
The ESERA eBUS Coupler Ethernet is well described in the manual.
Software
ebusd installation
From: https://github.com/john30/ebusd-debian/blob/master/README.md 2
Add the GPG key to your trusted apt sources (usually root access required):
wget -qO - https://raw.githubusercontent.com/john30/ebusd-debian/master/ebusd.gpg.key|apt-key add –
Copy the right source list for your architecture (check by executing dpkg –print-architecture) to /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ (replace ARCH with either amd64, armhf or i386):
wget -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ebusd.list https://raw.githubusercontent.com/john30/ebusd-debian/master/ebusd-ARCH-default.list
If you prefer the variant without MQTT support, use this command instead (replace ARCH with either amd64, armhf or i386):
wget -O /etc/apt/sources.list.d/ebusd.list https://raw.githubusercontent.com/john30/ebusd-debian/master/ebusd-ARCH-nomqtt.list
After that, you can simply update the package lists via apt-get update(depending on your distribution) and then install with apt-get install ebusd.
Setup ebusd
(My revision of) the VRT350 is not supported at this time (30-Dec-2021) by the ebus config files. (Incomplete) support has been added in this pull request. Hence copy these files. E.g. to: /home/openhabian/ebusd-configuration/ebusd-2.1.x/en/
Configure ebusd to connect to the ESERA eBUS coupler and use the copy of the configuration files by setting the EBUSD_OPTS in /etc/default/ebusd. Here’s an excerpt from my config:
EBUSD_OPTS="-d ebuscoupler.localdomain:5000 --scanconfig -c /home/openhabian/ebusd-configuration/ebusd-2.1.x/en/"
Optionally test ebusd by manually starting ebusd on the command line with the arguments from /etc/default/ebusd. Add -f to run in foreground. Test reading from ebus by executing “ebusctl read Hc1DayTemp” in a different terminal.
Configure systemd to start ebusd automatically:
sudo systemctl enable ebusd
Configure thing(s) in OpenHAB
Install Exec Binding
Add to things:
Thing exec:command:ebusctl_write_DesiredTemp "BeganeGrond:Woonkamer:CV_gewenste_temperatuur_schrijven" [command="ebusctl write -c 350 Hc1DayTemp %2$s", interval=0, autorun=true]
Possible future improvements
- Serial data packing conditions > 1ms
Alternatives considered
- BUS: OpenTHERM → not chosen as this would require exchaning the thermostat.
- Valliant support.
- OpenTherm gataway.
- eBUS interface
- ESERA eBus Coupler USB
- eBUS Adapter 3. Pro’s: WiFi, automatic adjustment of eBUS voltages. Cons: PCBs: not available when I was performing my installation.
- eBUS plugins for OpenHAB
- eBUS Binding v1 → outdated
- eBUS 2.0 binding, development continued here → Not included in OpenHAB release. Not as feature rich as ebusd (e.g. grab command).
Recognition
This work is based on numerous others, including: OpenHAB, ebusd, the OpenHAB forum. Thanks!
Notes
- ebusd wiki describes the ebusd and command line tools in detail:
- Valliant write command is b5 09 0D. Valliant read command is b5 09 0E. See vaillant_ebus_v0.6.0.pdf.
- Use grab command in ebusctl to decode data in multiple formats. Read the data first using a hex command and remove the address from the configuration files to avoid “normal” interpretation.
- To read in hex start ebusd with –enablehex.
- write
>> ebusctl write -c 350 Hc1DayTemp 19.0 - read
>> ebusctl read Hc1DayTemp - 350 is the name of the thermostat. See xml_config_files.
- read hex
>> ebusctl hex 15b509030d0000
History
2021-06-15 - Original blogpost
2021-12-30 - Updated pull request with configuration files. The VRT350 configuration file now supports more features of the VRT350.